- Головна
- Готові шкільні презентації
- Презентація на тему «H.I.V.»
Презентація на тему «H.I.V.»
266
Слайд #1
H.I.V.
By Karina Ocheretyana
By Karina Ocheretyana

Слайд #2
WHAT IS HIV??
“Human Immunodeficiency Virus”
A unique type of virus (a retrovirus)
Invades the helper T cells (CD4 cells) in the body of the host (defense mechanism of a person)
Threatening a global epidemic.
Preventable, managable but not curable.
“Human Immunodeficiency Virus”
A unique type of virus (a retrovirus)
Invades the helper T cells (CD4 cells) in the body of the host (defense mechanism of a person)
Threatening a global epidemic.
Preventable, managable but not curable.

Слайд #3
WHAT IS AIDS ???
“Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome”
HIV is the virus that causes AIDS
Disease limits the body's ability to fight infection due to markedly reduced helper T cells.
Patients have a very weak immune system (defense mechanism)
Patients predisposed to multiple opportunistic infections leading to death.
“Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome”
HIV is the virus that causes AIDS
Disease limits the body's ability to fight infection due to markedly reduced helper T cells.
Patients have a very weak immune system (defense mechanism)
Patients predisposed to multiple opportunistic infections leading to death.

Слайд #4
AIDS (definition)
Opportunistic infections and malignancies that rarely occur in the absence of severe immunodeficiency (eg, Pneumocystis pneumonia, central nervous system lymphoma).
Persons with positive HIV serology who have ever had a CD4 lymphocyte count below 200 cells/mcL or a CD4 lymphocyte percentage below 14% are considered to have AIDS.
Opportunistic infections and malignancies that rarely occur in the absence of severe immunodeficiency (eg, Pneumocystis pneumonia, central nervous system lymphoma).
Persons with positive HIV serology who have ever had a CD4 lymphocyte count below 200 cells/mcL or a CD4 lymphocyte percentage below 14% are considered to have AIDS.

Слайд #5
Modes of HIV/AIDS Transmission

Слайд #6
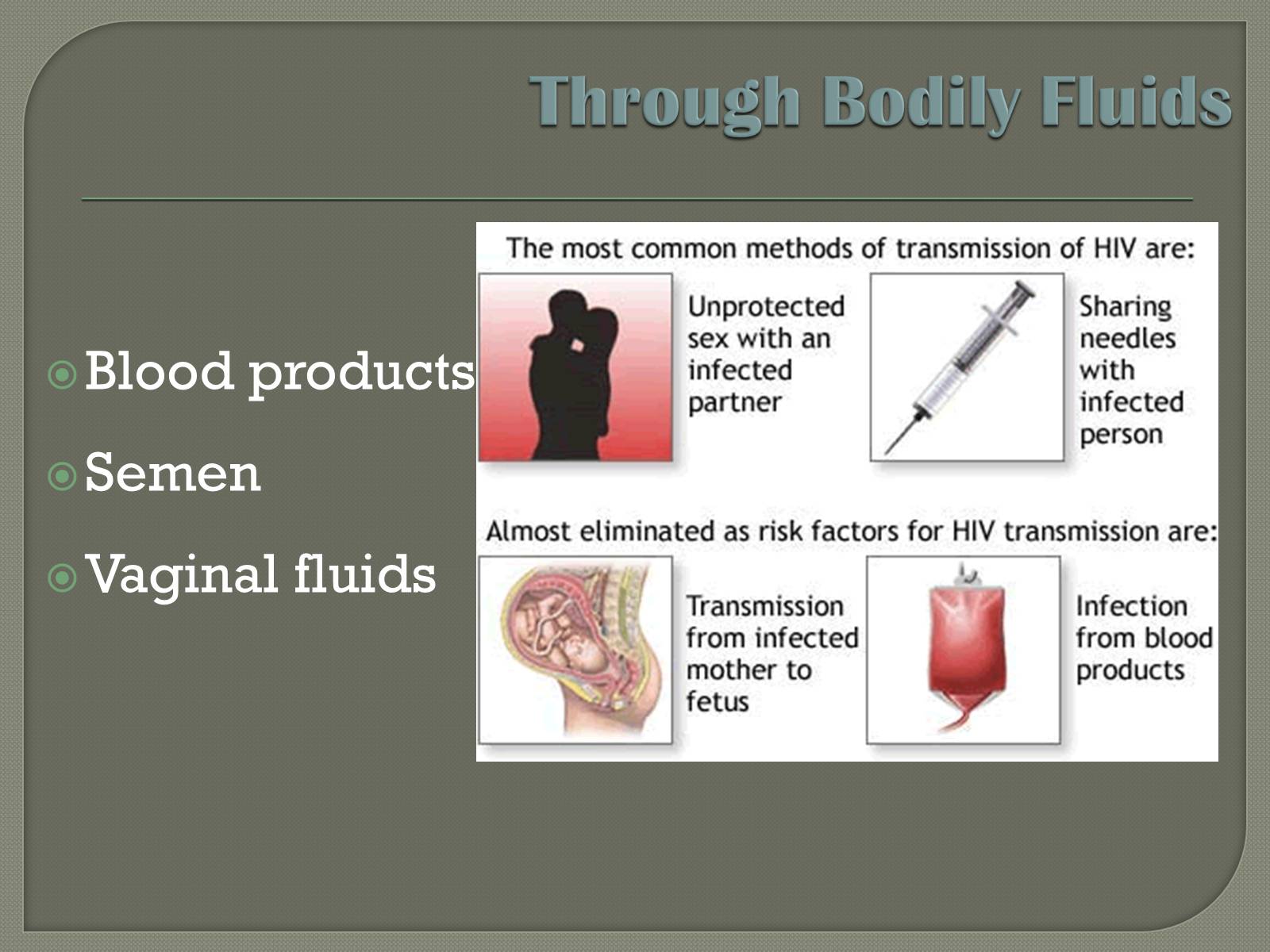
Through Bodily Fluids
Blood products
Semen
Vaginal fluids
Blood products
Semen
Vaginal fluids
Слайд #7
IntraVenous Drug Abuse
Sharing Needles
Without sterilization Increases the chances of contracting HIV
Unsterilized blades
Sharing Needles
Without sterilization Increases the chances of contracting HIV
Unsterilized blades

Слайд #8
Through Sex
Unprotected Intercourse
Oral
Anal
Unprotected Intercourse
Oral
Anal

Слайд #9
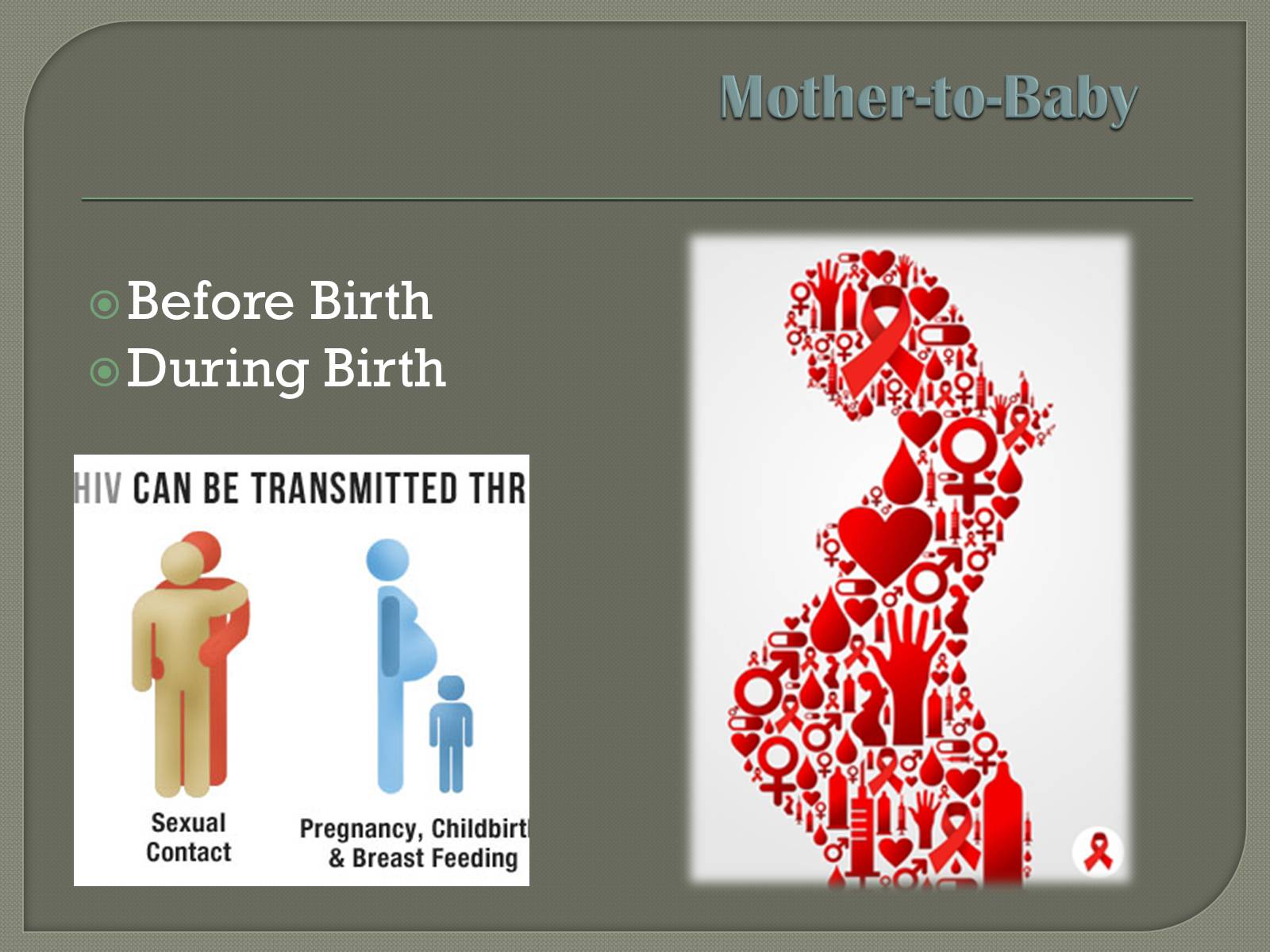
Mother-to-Baby
Before Birth
During Birth
Before Birth
During Birth
Слайд #10
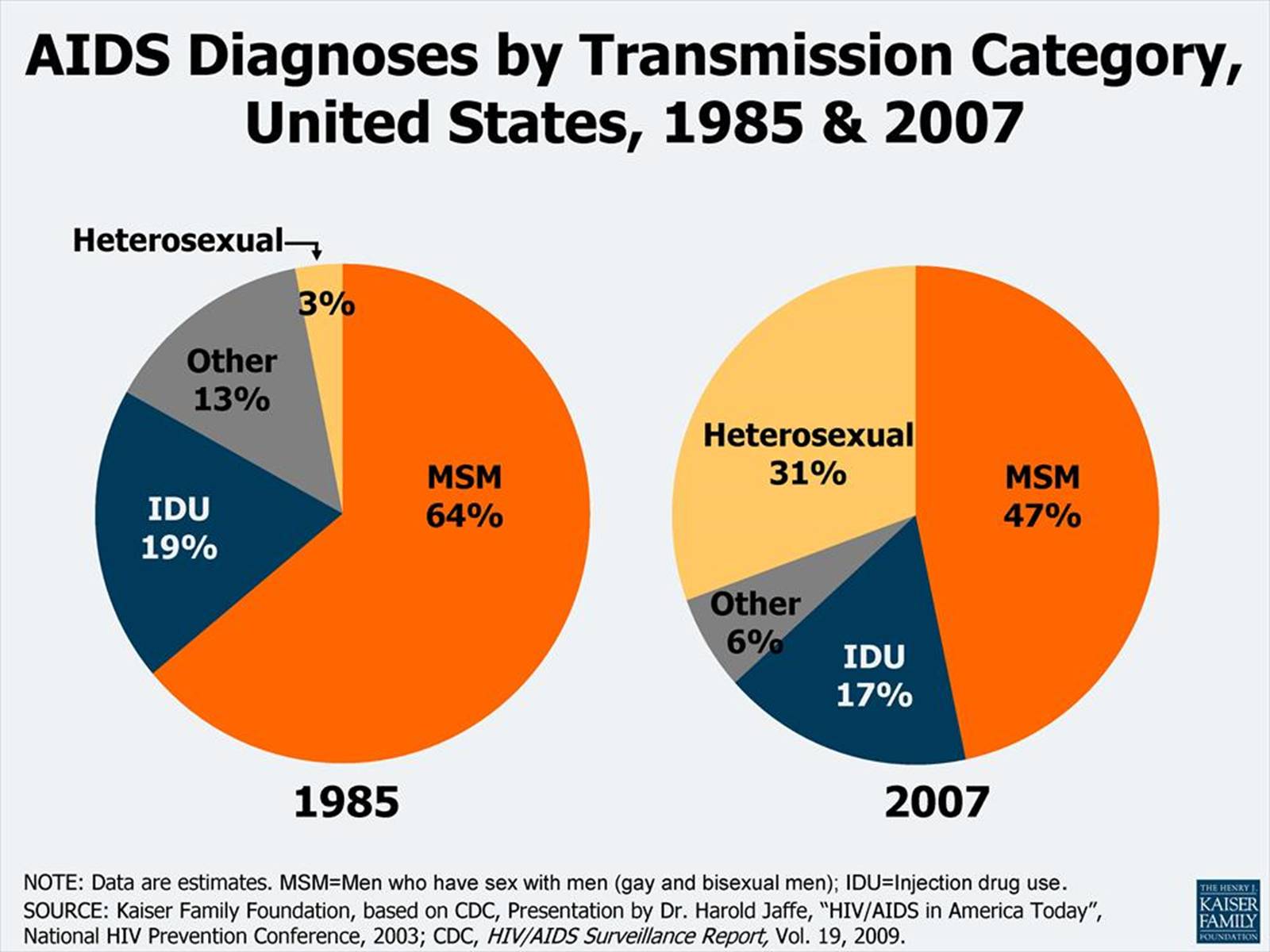
Myths about transmission

Слайд #11
Myths about transmission
Слайд #12
PRIMARY PREVENTION:4 ways to protect yourself?
Abstinence
Protected Sex
Sterile needles
New shaving/cutting blades
Abstinence
Protected Sex
Sterile needles
New shaving/cutting blades

Слайд #13
Abstinence
It is the most effective method of not acquiring HIV/AIDS.
Refraining from unprotected sex: oral, anal, or vaginal.
Refraining from intravenous drug use
It is the most effective method of not acquiring HIV/AIDS.
Refraining from unprotected sex: oral, anal, or vaginal.
Refraining from intravenous drug use

Слайд #14
Protected Sex
Use condoms every time you have sex
Always use latex or polyurethane condom (not a natural skin condom)
Always use a latex barrier during oral sex
Use condoms every time you have sex
Always use latex or polyurethane condom (not a natural skin condom)
Always use a latex barrier during oral sex

Слайд #15
When Using A Condom Remember To:
Make sure the package is not expired
Make sure to check the package for damages
Do not open the package with your teeth for risk of tearing
Never use the condom more than once
Use water-based rather than oil-based condoms
Make sure the package is not expired
Make sure to check the package for damages
Do not open the package with your teeth for risk of tearing
Never use the condom more than once
Use water-based rather than oil-based condoms

Слайд #16
HIV PREVALENCE IN VARIOUS REGIONS
Source: UNAIDS, AIDS Epidemic Update, December 2004.
Total = 39.4 million
Sub-Saharan Africa
South/South-East Asia
Oceania
Caribbean
North Africa/Middle East
Western Europe
North America
East Asia
Eurasia
Latin America
<
42%
Source: UNAIDS, AIDS Epidemic Update, December 2004.
Total = 39.4 million
Sub-Saharan Africa
South/South-East Asia
Oceania
Caribbean
North Africa/Middle East
Western Europe
North America
East Asia
Eurasia
Latin America
<
42%

Слайд #17
WHAT WE CAN DO??
UNAIDS Outcome Framework 2009–2011: nine priority areas
We can reduce sexual transmission of HIV.
We can prevent mothers from dying and babies from becoming infected with HIV.
We can ensure that people living with HIV receive treatment.
We can prevent people living with HIV from dying of tuberculosis.
We can protect drug users from becoming infected with HIV.
We can remove punitive laws, policies, practices, stigma and discrimination that
block effective responses to AIDS.
We can stop violence against women and girls.
We can empower young people to protect themselves from HIV.
We can enhance social protection for people affected by HIV.
UNAIDS Outcome Framework 2009–2011: nine priority areas
We can reduce sexual transmission of HIV.
We can prevent mothers from dying and babies from becoming infected with HIV.
We can ensure that people living with HIV receive treatment.
We can prevent people living with HIV from dying of tuberculosis.
We can protect drug users from becoming infected with HIV.
We can remove punitive laws, policies, practices, stigma and discrimination that
block effective responses to AIDS.
We can stop violence against women and girls.
We can empower young people to protect themselves from HIV.
We can enhance social protection for people affected by HIV.

Слайд #18
LIVING WITH HIV/AIDS

Слайд #19
LIVING WITH HIV/AIDS

Слайд #20
THE END
